
New Advances in Understanding Lithium-Beryllium Rare Metal Mineralization in the West Kunlun
Publisher:
time: 2025-12-30
Recently, the research team led by CAS Academician Xiao Wenjiao published new findings in Ore Geology Reviews. The study systematically reveals the key mechanisms of lithogenesis and mineralization for lithium-beryllium rare metals in the Dahongliutan area of the West Kunlun orogenic belt. Focusing on the granitic parent rocks of typical Li-Be deposits in the region, the research uses comprehensive petrological, geochemical, and isotopic chronological analyses to elucidate the genetic relationships between rock formation, magmatic evolution, and regional Li-Be mineralization.
The study indicates that the parent granite of the 509 Daobanxi Li-Be deposit formed during the Late Triassic (206–205 Ma). It is an S-type granite derived from the partial melting of Triassic clay-rich pelitic metasedimentary rocks. Significant crystallization differentiation during magmatic evolution drove the high enrichment and mineralization of rare metals such as lithium and beryllium. This magmatic-mineralization event is closely related to the crustal extensional setting following the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. The findings further reveal that the clay-rich pelitic metasedimentary source, external thermal drivers, and highly fractionated rare-metal granites are key controlling factors for Li-Be rare metal mineralization in this region.
This achievement deepens the scientific understanding of regional tectono-magmatic-metamorphic-mineralization coupling, advances the theory of pegmatite-type Li-Be ore formation in the Tethyan tectonic domain, and provides crucial theoretical support for the exploration and efficient development of strategic rare metal resources like lithium and beryllium. This is of significant importance for enhancing China's security capabilities regarding strategic key mineral resources.
The research was supported by CPJRC.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2025.106769
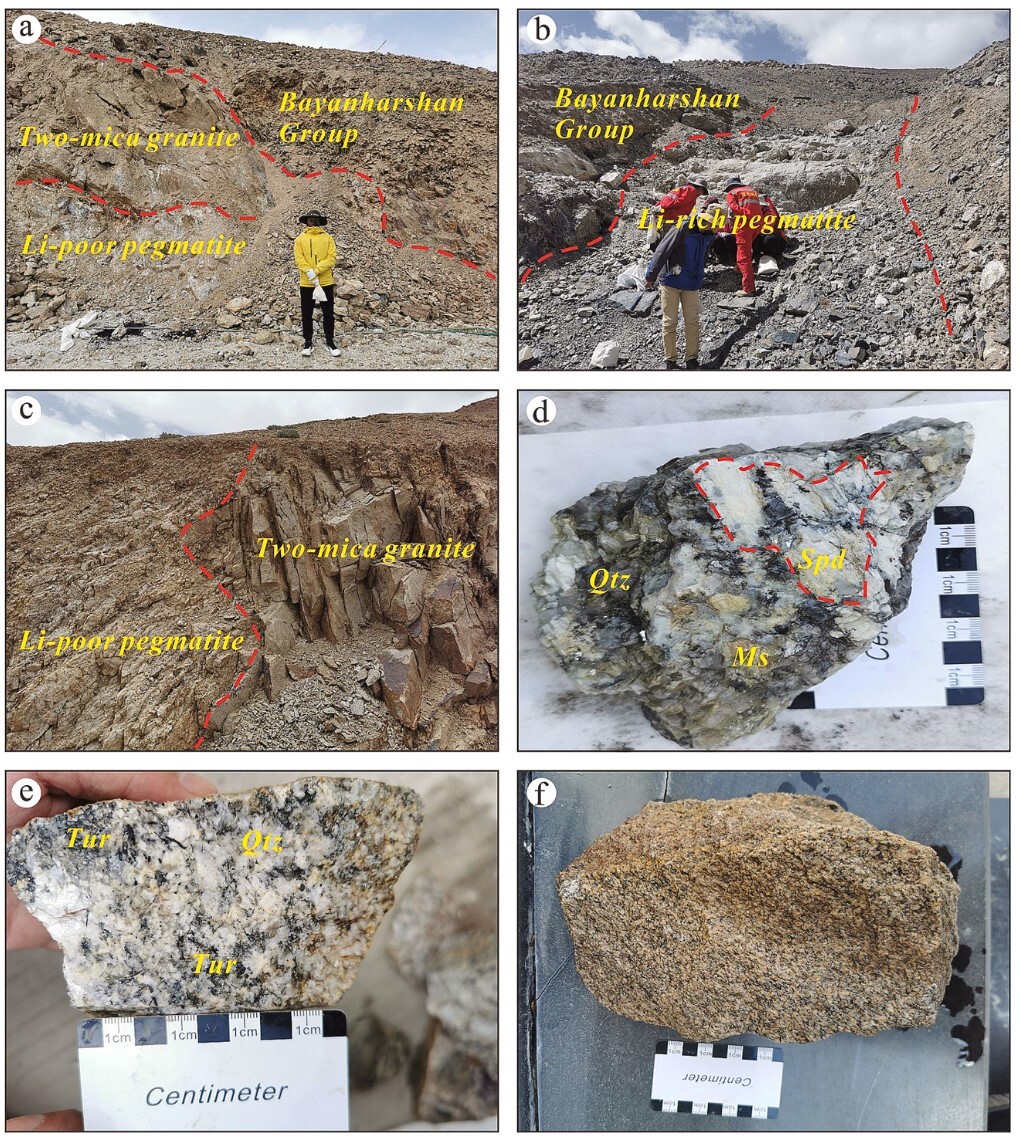

Fieldtrip of Li-rich/Li-poor Pegmatites in the Dahongliutan Area
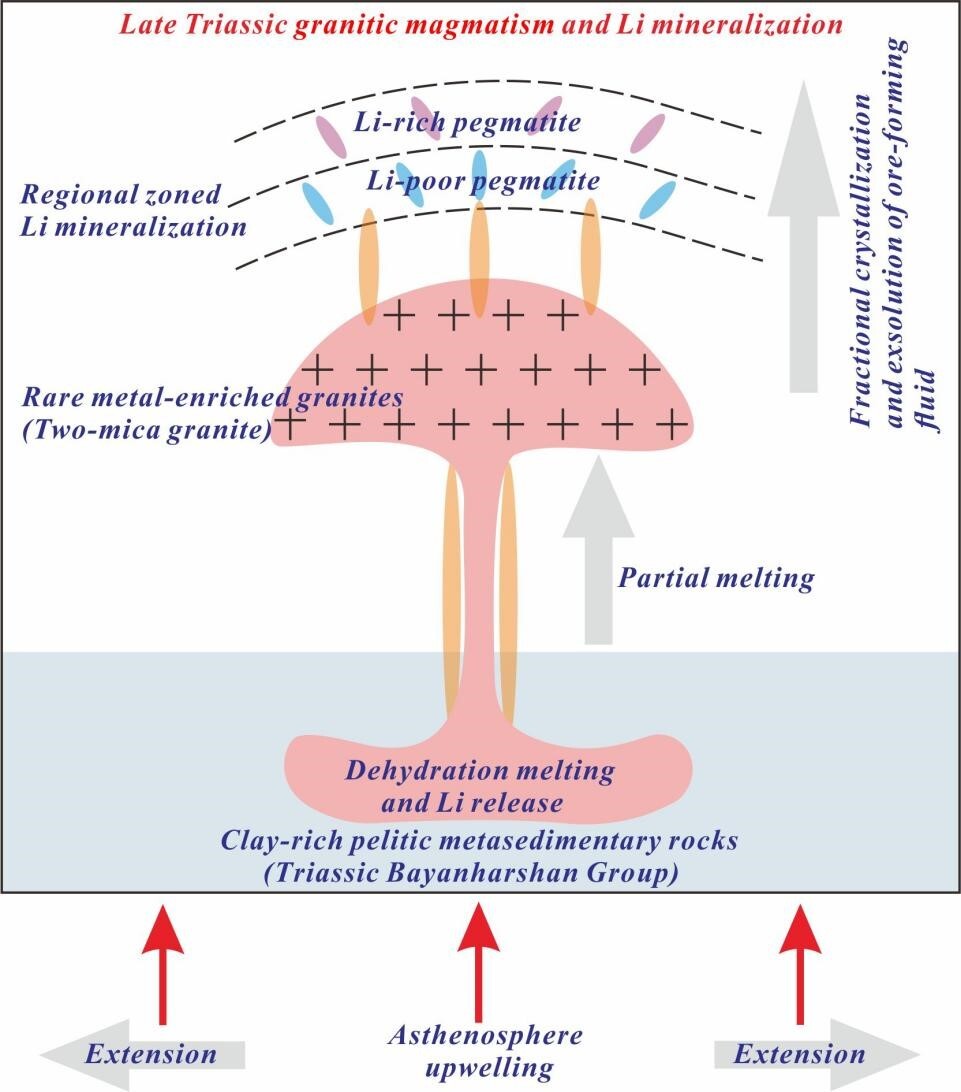
Mineralization Model of Late Triassic Pegmatite-Type Rare Metal Deposits in the Dahongliutan Area, West Kunlun