
New Progress Has Been Made in Groundwater Depletion Monitoring of the District Faisalabad Pakistan
Publisher:
time: 2022-07-22
The research group of Prof. Juanle Wang, the fourth researcher of the China-Pakistan Center, has made new progress in the research on the monitoring of groundwater depletion in the district of Faisalabad Pakistan. The relevant research results were recently published online in "atmosphere".
The sustainable development in water resource management in the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor is a prerequisite for ensuring the safety of related energy projects for drinking and irrigation water. It has been observed that the increasing demand for groundwater in urban and agricultural sectors and the instability of groundwater ecosystems has threatened water security, food security, and ecological security not only this but the instant exploration of groundwater causes land surface deformation. Which is an alarming situation for sustainable development in the region. Groundwater depletion and change in groundwater level information refer to the continuous information of time series wells data in the region which has been continuously monitored throughout the year. Obtaining this information is an important basis for formulating policies for the sustainable development of regional groundwater resources management and the environment.
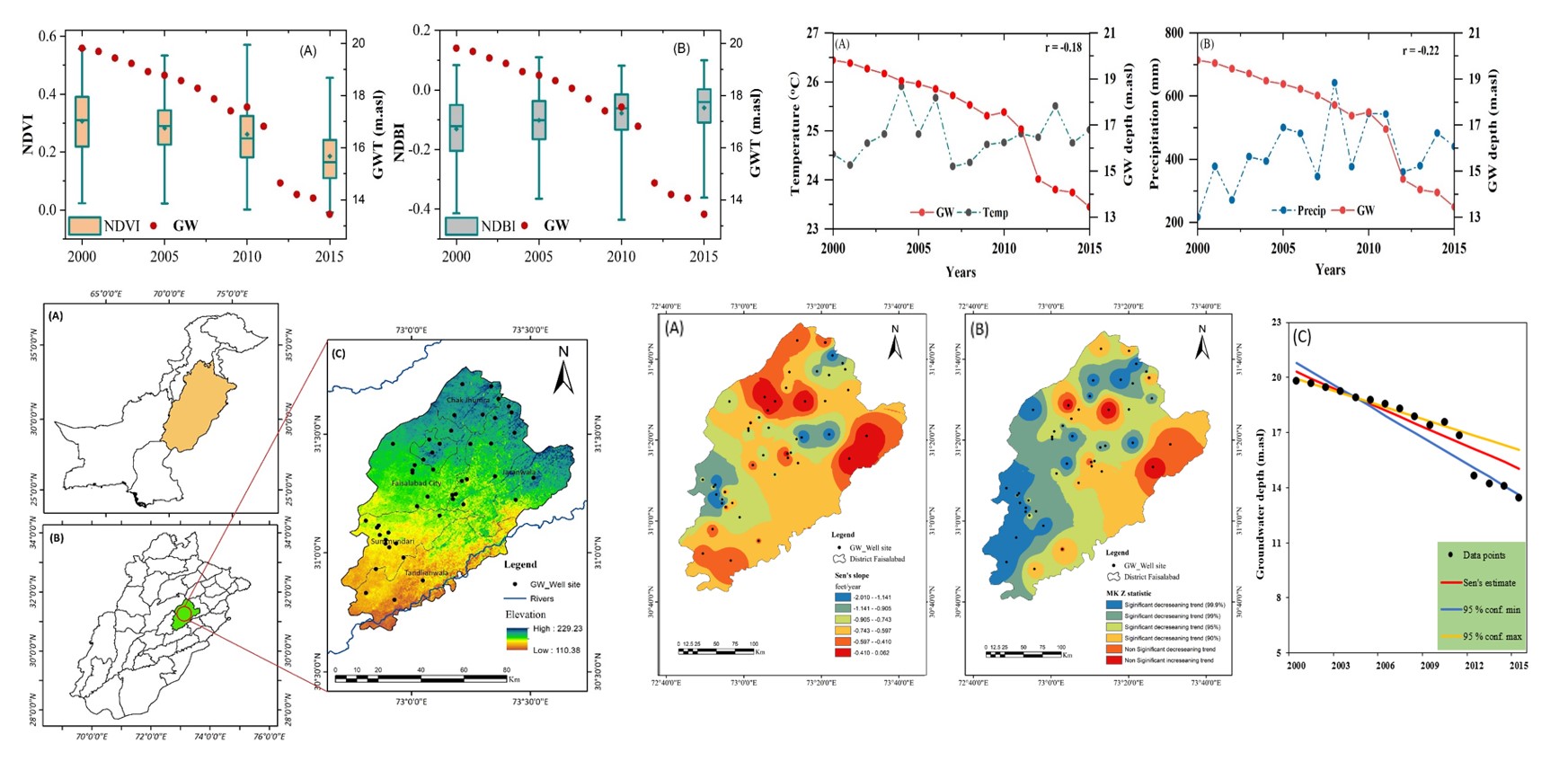
Focusing on these major issues, Prof. Juanle Wang's research group used the Mann–Kendall test and Sens’s slope combined with remote sensing, Landsat images, to monitor the groundwater depletion and the impact of land use change in the district of Faisalabad Pakistan. The Landsat high-resolution imagery of 5 & 8 data for the land use change cover of NDBI and NDVI in the region combined with climatic parameters of precipitation and temperature from 2000 to 2015, to monitor the groundwater depletion in the district Faisalabad Pakistan.
The research results show that, during the fifteen years from 2000 to 2015, over the time the build-up area has continuously increased and vegetation has been decreased, meanwhile, the groundwater level in the region also showed a significant downward trend due to the over-extraction of groundwater by people need. From 2000 to 2015 the average groundwater level has been depleted by approximately 0.11 m/year. Overall, spatial analysis results showed a statistically positive trend in the groundwater level of the Faisalabad district, where the NDBI ratio is high and the NDVI is low, owing to the extensive extraction of groundwater for domestic and industrial use Climatic parameters (i.e., precipitation and temperature) further reveal an insignificant increasing trend.
The research provides an important data basis and monitoring method for planning groundwater resource management, protecting environmental degradation, and promoting regional sustainable development of water demand in the urban and agricultural sectors of the China-Pakistan Corridor in the major cities of Pakistan.
The research was funded by the China-Pakistan Earth Science Research Center.
Article DOI: 10.3390/atmos13071097

Related Information of the Article